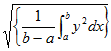User Guide/Appendix/Amplitude Measurements, Root Mean Square Value, VRMS: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:{{SUBPAGENAME}}}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:{{SUBPAGENAME}}}} | ||
{{Appendix}} | |||
The RMS value of an alternating current is that current which will give the same heating effect as the equivalent direct current. The RMS value of y=f(x) over the range x=a to x=b is given by: | The RMS value of an alternating current is that current which will give the same heating effect as the equivalent direct current. The RMS value of y=f(x) over the range x=a to x=b is given by: | ||
Revision as of 15:58, 7 September 2015
The RMS value of an alternating current is that current which will give the same heating effect as the equivalent direct current. The RMS value of y=f(x) over the range x=a to x=b is given by:
The mean or average value of a waveform between x=a to x=b is given by:
For simple tones (sinusoidal waveforms) the relationships between RMS value, AVG value, peak and peak-to-peak value are given in Table 6.
| from value | multiplication factor to value | ||||
| average | RMS | peak | peak-to-peak | ||
| average | 1.0 | 1.11 | 1.57 | 3.14 | |
| RMS | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.414 | 2.828 | |
| peak | 0.637 | 0.707 | 1.0 | 2.0 | |
| peak-to-peak | 0.32 | 0.3535 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
Table 6: Peak-to-peak, RMS and AVG value conversion for sinusoidal waveforms:{| |- | | | | | | | | |- |Coding bits/sample: n |8 |16 |18 |20 |22 |24 |32 |- |FS ratio: N/1 |28 |216 |218 |220 |222 |224 |232 |- |FS ratio: dB |48 |96 |108 |120 |132 |144 |192 |- |Note: dB (FS) = 20 * lg(N) = 20 * lg(2n) = 20*0.3010*n |}
Table 7. Full Scale Range (dB FS) available at different digital word lengths (bits/sample).