Programmer Guide/SPU Reference/SSIGIN: Difference between revisions
m 1 revision: Initial import |
|
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 11:14, 28 April 2011
Contents
SSIGIN - read signal (for filters, ...)
Usage:
SSIGIN SIG REV L S K D
Inputs:
| SIG | name of shell-wave-item | no default |
| REV | 0, YES|1)
|
def.=NO |
| L | frame length in samples (>=4) | def.=1024 |
| S | frame shift in samples (1 <= S <= L) | def.=L/4 |
| K | amplification factor | def.=1 |
| D | differentiation factor (0..1) | def.=0 |
Outputs:
| Xi | signal of channel i (L samples) |
| SR | sampling rate in Hz |
| N | number of frames |
| I | frame counter (0..N) |
Function:
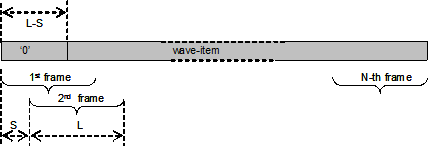
This atom implements an alternative signal-frame read function that can be used instead of CSIGN. The frame-splitting method is designed to be used for filter or other frequency-domain processing methods. The partitioning of the signal is similar to the method used by the phase vocoder, but no windowing or other processing is applied to the frames. The picture below shows the frame partitioning method:
Frame partitioning method used by SSIGIN=====Notes:=====
This read function is currently not used, because specialized signal-I/O (analysis/re-synthesis) atoms for the filter methods have been implemented. The values of the outputs SR and N are set during the initialization. The output I is initialized to 0 and incremented by 1 after each read cycle. The input REV can be used to reverse the signal in time.