Programmer Guide/SPU Reference/SSIGIN: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|- | |- | ||
!RSIGIN | !RSIGIN | ||
| | |Random read. Read signal frame centered around position <var>POS</var>. | ||
| | |<math>POS-L/2 .. POS+L/2-1</math><BR><math>0 \leqslant | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:47, 10 May 2011
Read/write signal from/to a wave item.
[SPU RSIGIN SIG REV L POS K D TYP OUT X1 .. X8 SR XMAX]
[SPU ASIGIN SIG REV L K D TYP OUT X1 .. X8 SR N I XMAX]
[SPU CSIGIN SIG REV L S K D TYP OUT X1 .. X8 SR N I XMAX]
[SPU SSIGIN SIG REV L S K D TYP OUT X1 .. X8 SR N I XMAX]
| description | frame position | |
|---|---|---|
| RSIGIN | Random read. Read signal frame centered around position POS. | POS−L/2..POS+L/2−1 Failed to parse (syntax error): {\displaystyle 0 \leqslant |} ==<code>[SPU SIGOUT <var>SIG X1 .. X8</var> OUT <var>SR I XMAX</var>]</code>== {|class="einrahmen" !input !!description !!data type !!value type!!default value |- |<var>A</var>||input data ||number, vector ||variable |- |<var>B</var>||masker or threshold ||number, vector ||variable |- |<var>C</var>||replacement data ||number, vector ||variable |- |<var>COND</var>||condition ||number (int.), string ||variable ||<code>0</code> |- !output !!description !!data type !!value type!!comment |- |<var>Y</var>||masked data ||same type as <var>A</var> ||variable |} ;Description: If the condition defined by <var>COND</var> is true, <var>C</var><sub>i</sub> is assigned to <var>Y</var><sub>i</sub>, otherwise <var>Y</var><sub>i</sub> is set to <var>A</var><sub>i</sub>. If <var>A</var> is a vector, the inputs <var>B</var> and <var>C</var> can be numbers or vectors with the same length as <var>A</var>. The output <var>Y</var> has always the same type as <var>A</var>. {|class="einrahmen" !<var>COND</var> !!Assignment |- |<code>0</code> or <code><</code> |<math>Y_i=\begin{cases} C_{[i]} & \mbox{if }A_i < B_{[i]} \\ A_i & \mbox{otherwise} \end{cases} } |
1 or >
|
Yi={C[i]if Ai>B[i]Aiotherwise | |
2 or ≤
|
Yi={C[i]if Ai⩽B[i]Aiotherwise | |
3 or ≥
|
Yi={C[i]if Ai⩾B[i]Aiotherwise |
with: 0 ≤ i < length of A; [i] means: index is used only if the input is a vector
- See also
<SP-atoms>
SSIGIN - read signal (for filters, ...)
Usage:
SSIGIN SIG REV L S K D
Inputs:
| SIG | name of shell-wave-item | no default |
| REV | 0, YES|1)
|
def.=NO |
| L | frame length in samples (>=4) | def.=1024 |
| S | frame shift in samples (1 <= S <= L) | def.=L/4 |
| K | amplification factor | def.=1 |
| D | differentiation factor (0..1) | def.=0 |
Outputs:
| Xi | signal of channel i (L samples) |
| SR | sampling rate in Hz |
| N | number of frames |
| I | frame counter (0..N) |
Function:
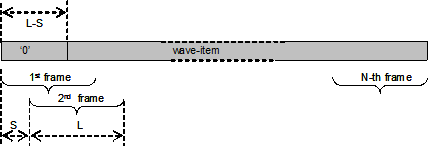
This atom implements an alternative signal-frame read function that can be used instead of CSIGN. The frame-splitting method is designed to be used for filter or other frequency-domain processing methods. The partitioning of the signal is similar to the method used by the phase vocoder, but no windowing or other processing is applied to the frames. The picture below shows the frame partitioning method:
Frame partitioning method used by SSIGIN=====Notes:=====
This read function is currently not used, because specialized signal-I/O (analysis/re-synthesis) atoms for the filter methods have been implemented. The values of the outputs SR and N are set during the initialization. The output I is initialized to 0 and incremented by 1 after each read cycle. The input REV can be used to reverse the signal in time.